Photo courtesy of NBC News
Sri Lanka has a whopping 527 state-owned enterprises[1] (SOEs). The 55 SOEs classified as “strategically important” alone employ 10% of the public sector workforce[2] or about 1.9% of all workers. Such a large number of SOEs are not the norm globally[3]; many other countries, such as India, have been reducing their stakes in SOEs and in some cases, such as Air India, have been privatizing them entirely. SOEs – particularly many in Sri Lanka – tend to be grossly inefficient, loss making and a burden on the taxpayer. The time is ripe for major SOE reforms.
What is an SOE?
A SOE is traditionally defined as a commercial entity that has majority ownership/control by a nation’s government. In Sri Lanka this can include statutory bodies, regulatory agencies, promotional institutions, educational institutions, public and limited companies. While SOEs have traditionally been incorporated by an Act of Parliament, in recent years these entities have been incorporated under the Companies Act instead. SOEs can be divided into three categories: 55 Strategic SOEs, 287 SOEs with commercial interests, and 185 SOEs with non-commercial interests. Unlike nations such as India that mandate internal audits of their SOE’s business activities and publish an annual overview with a balance sheet of each individual business, the majority of Sri Lankan SOEs do not reveal this information to the public; financial information is available for just 10.4% of SOEs.
Fundamental problems with SOEs
Contrary to what some believe, low quality of talent is not the most significant issue with SOEs; many employees are eminently qualified and capable. Unfortunately, these organizations fall victim to government mismanagement and corruption. In addition to excessive employment to fulfill their political ambitions, there have been allegations that some SOEs have been formed purely to facilitate corruption, for example, the Lanka Coal Company engaged in fraudulent deals to purchase coal causing a loss of over Rs. 4 billion, allegedly with the knowledge of the minister in charge. SOE financials are late and few obtain clean audit reports. Investigations have revealed repeated instances of fraud, mismanagement, corruption and negligence. Furthermore the internal control, monitoring and governance frameworks seem inadequate to deal with these problems; of over 500 SOEs, regular information is only available for 55. Even obtaining a complete list of entities proved to be a challenge. Public access to information is limited. The Department of Public Enterprises has not released an annual report since 2018 and right to information requests often go unanswered.
Trends in labor productivity of SOEs (2010-2018)
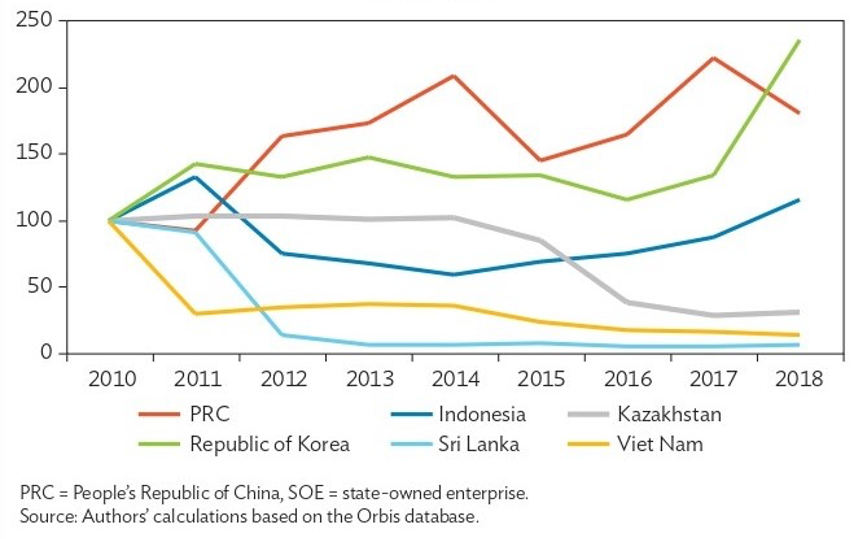
Source: Ginting, Edimon et al, 2020, Reforms, Opportunities, and Challenges for State-Owned Enterprises, Asian Development Bank
SOEs have few budget constraints and shareholder (public) accountability and therefore have limited incentive to control costs. Unlike private sector enterprises, which have a need to make a profit, many SOEs can simply borrow from other state organizations and banks or the government when they require additional funds, which undermines the threat of bankruptcy as a source of discipline[4]. Some recently established SOEs have found a new way of bypassing budgets and oversight; by incorporating as companies rather than through an act of Parliament, they are excluded from parliamentary accountability and allowed to rack up unsustainable debts and surpass budgets more easily. This has led to SOEs burning through taxpayer rupees. The cumulative losses of the 55 strategic SOEs from 2006-20 amounts to Rs. 1.2 trillion.
While some SOEs do manage to make a profit this is due to the advantage that these companies have in an uneven playing field. In addition to lax budgetary requirements and ability to rack up unsustainable debts, these companies are supported by the government through direct subsidies and state-backed guarantees, by regulators through exemptions from antitrust policies and preferential treatment and by the justice system through an ability to sidestep parliament. This has led to private sector organizations being crowded out of the industries that SOEs operate in. Instead of having private firms in the market place with efficient and high quality services, the taxpayer is beset with SOEs with total liabilities of 4 to 5% of GDP.
Potential reforms
Given that the nation has reached an economic tipping point with serious questions about debt sustainability and government solvency, it is clear that immediate action must be taken. Advocata proposes a short term policy solution consisting of privatization, restructuring and disinvestment and listing on the Colombo Stock Exchange. None of these solutions are particularly radical in the global or local context. According to Anarkali Moonesinghe, Director of the Lankan Angel Network, the two main policies of both Western and Eastern governments when reforming SOEs are to reduce subsidies and increase efficiency, forcing SOEs to compete more equitably with private enterprises. Alternatively, full or partial privatization is a possible solution. SLT Mobitel’s service has markedly improved following its 1997 privatization and the entrance of competitors such as Dialog Axiata, all held accountable by the broadly competent Telecommunications Regulatory Commission. Listing on the CSE would allow these firms to have broad-based direct ownership, while also improving the growth of the CSE and capital markets. Importantly, these firms would have to be corporatized before listing, an opportunity to improve productivity and eliminate bloat. There are firms that will essentially have to be given away due to their huge debts and poor reputations. A prime example of this is Sri Lankan Airlines, which has racked up Rs. 316 billion in losses since control was taken from Emirates in 2008. While some will regard this as a blow to our national pride, Sri Lanka would not be alone in taking such a pragmatic step to improve government finances and customer experience; Air India, the Indian national carrier, is currently in the process of being sold to the Tata Group for a relatively small sum. This would inspire confidence among foreign investors as it would show the country’s commitment to meeting its upcoming debt servicing obligations.
Long term solutions include strengthening governance and limiting corruption and influence, improving efficiency, enacting cost-reflective pricing, and finally unbundling key sectors. This applies particularly to firms like the Ceylon Electricity Board which, as a natural monopoly, cannot be broken up and privatized without losing efficiency. A 2006 study by the Japan International Cooperation Agency recommended breaking up CEB into three parts: “making the generation, transmission, and distribution divisions…independent”[5]. Despite the 15 years and multiple nationwide blackouts that have occurred since, the government continues to drag its feet on the issue as it is politically unpopular. Cost-reflective pricing (also prevented due to political unpopularity) is another essential reform. The existing system of having electricity tariffs priced below cost is a public subsidy whose cost will be borne by future generations. It is also inequitable, as the government could provide low cost services to those who need it by giving them direct cash transfers instead of subsidizing the wealthy who can afford to pay. A similar situation is evident with the Ceylon Petroleum Corporation, which currently makes a loss of Rs. 23 to 38 per liter of fuel; again, a public subsidy to those who can often afford to pay the market price. Finally greater accountability, by means of annual internal audits and the availability of SOEs’ financial information to the public, is also important to ensure these firms stick to the targets they are given.
A successful and thriving market will only occur with the presence of three crucial factors: competition, a good framework, and competent regulation. By reforming Sri Lanka’s SOEs to meet these criteria, we will ensure a good customer experience, a reduction in the government deficit and general prosperity for all key stakeholders.
[1] Ratnsabapathy, Ravi et al, 2019, The State of State Enterprises in Sri Lanka, Advocata Institute
[2] Dissanayake, Imesha, 2021, SOE Reforms; the Impetus for Post Pandemic Economic Revival, Ceylon Chamber of Commerce
[3] Büge, Max et al, State-owned enterprises in the global economy: Reason for concern?, Last modified: May 2nd, 2013
[4] Ratnsabapathy, et al,The State of State Enterprises in Sri Lanka,
[5] Saito, Yoshitaka et al, 2006, Master Plan Study on the Development of Power Generation and Transmission System in Sri Lanka, Japan International Cooperation Agency Economic Development Department
Migara Rodrigo is a Researcher at the Advocata Institute.


